Cytochrome P450 2B6

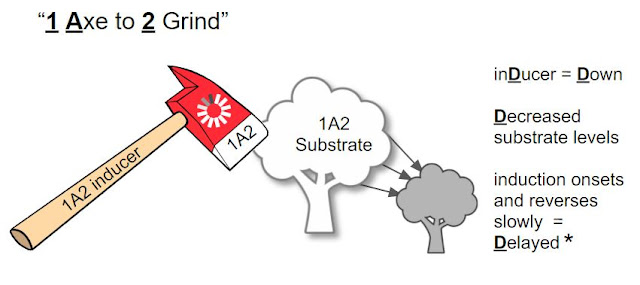
Excerpt from Cafer's Mood Stabilizers and Antiepileptics Cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6) “Tube Socks” 3% of individuals are 2B6 ultrarapid metabolizers; 7% are poor metabolizers in D uction = D own D ecreased substrate levels induction onsets and reverses slowly, over 2 - 4 weeks = D elayed There are no strong 2B6 inducers. in H ibition = H igh in H ibition happens within H ours = H urried and reverses as soon as the inhibitor is cleared from the body (five half-lives of the inhibitor) There are no strong 2B6 inhibitors. Here are the 2B6 inducers: Here are the 2B6 inhibitors: Here are the 2B6 substrates: 3% of the population are 2B6 ultrarapid metabolizers (UMs). Methadone efficacy for these individuals will be poor, and their methadone drug screen may be negative. Conclusion: Fortunately, there are no strong inhibitors or inducers of 2B6. For psychiatrists, 2B6 is of minimal significance, unless methadone is b...